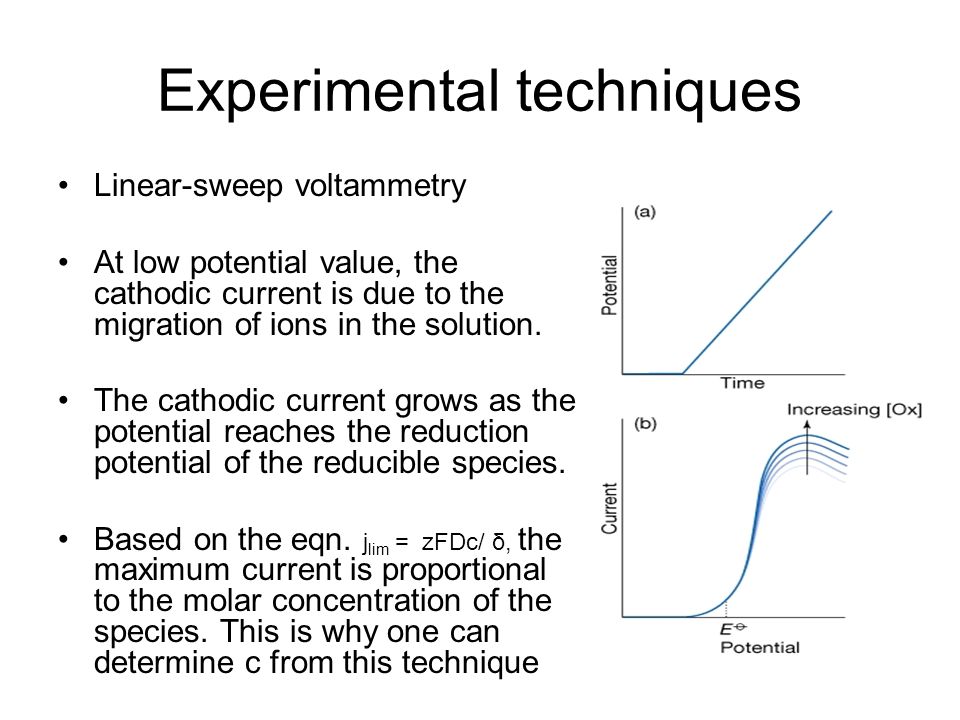
Experimental techniques Linear-sweep voltammetry At low potential value, the cathodic current is due to the migration of ions in the solution. The cathodic. - ppt download
$ 13.50 · 4.7 (572) · In stock
Cyclic voltammetry Determine the redox potential Reflect the underlying kinetics
The cathodic current grows as the potential reaches the reduction potential of the reducible species. Based on the eqn. j lim = zFDc/ δ, the maximum current is proportional to the molar concentration of the species. This is why one can determine c from this technique.
The output is the slope of a curve like that obtained by linear-sweep voltammetry.
CV spectrum, the sweeping rate and the underlying kinetics
The electroactive material is ClC 6 H 4 CN in acidic solution; after reduction to ClC 6 H 4 CN -1, the radical anion may form C6H5CN irreversibly. ClC 6 H 4 CN + e ↔ ClC 6 H 4 CN -1 ClC 6 H 4 CN -1 + H + + e → C 6 H 5 CN + Cl - C 6 H 5 CN + e ↔ C 6 H 5 CN -.
Electrolysis: To induce current to flow through an electrochemical cell and force a non-spontaneous cell reaction to occur. It requires that the applied potential difference exceed the zero-current potential by at least the cell overpotential. Estimating the relative rates of electrolysis..
The cell potential decreases as current is generated because it is then no longer working reversibly. Consider the cell M|M + (aq)||M’ + (aq)|M’ and ignore complications from liquid junctions. The potential of the cell E’ = ΔФ R - ΔФ L As ΔФ R = E R + η R ; ΔФ L = E L + η L E’ = E + η R - η L.
E’ = E – IRs – 4RT ln(I/9Aj))/F j = (j oL j oR ) 1/2 where j oL and j oR are the exchange current densities for the two electrodes (for single electron transfer and high overpotential) The concentration overpotential also reduces the cell potential see (8 th edition) or )7 th edition) The full expression for the cell potential when a current I is being drawn: see eqn a or
The dependence of the potential of a working cell on the current density being drawn (blue line) and the corresponding power output (IE)
In hydrogen/oxygen cell, the electrolyte used is concentrated aqueous potassium hydroxide maintained at 200 o C and atm. The cathode reaction is O 2 (g) + 2H 2 O(l) + 4e - → 4OH - (aq) Eo = 0.40V The anode reaction is oxidation H 2 (g) + 2OH - (aq) → 2H 2 O(l) + 2e - The overall reaction 2H 2 (g) + O 2 (g) → 2H 2 O(l) E = 1.23V The advantage of the hydrogen/oxygen system is the large exchange current density of the hydrogen reaction, but the oxygen reaction has a small exchange current density..
The thermodynamic discussion only indicates the tendency. The kinetic process shall also be examined..
Calculate the current density when the over potential is +5.0mV. What would be the current at pH = 2.0, the other conditions being the same. Solution: Step1: using Nernst equation to calculate E, Step 2: calculate η on the basis that there is no change in E’; η = E’ – E: step 3: J = j 0 fη.
calculate the current density for the ratio of activities α(Cr 3+ )/α(Cr 2+ ) in the range 0.1 to 10.0 and at 25 o C..

Comparative assessment of Ni–Co coatings obtained from a deep

Cyclic Voltammetry Basic Principles, Theory & Setup

11.4: Voltammetric Methods - Chemistry LibreTexts

Sensitive Electrochemical Sensor Based On an Aminated MIL-101(Cr
Surface-immobilized cross-linked cationic polyelectrolyte enables

Controlling basal plane sulfur vacancy in water splitting MoSx/NiF

Basic potential step and sweep methods

Membranes, Free Full-Text

Recent Advances in Voltammetry - Batchelor‐McAuley - 2015

전기화학 계측기, 전극, 전해 셀, 소모품 전문기업

Insights into the design of mildly acidic aqueous electrolytes for

Voltammetry - an overview